SAP HANA Security
What is SAP HANA Security ?
Security means protecting company’s critical data from unauthorized access and use, and to ensure that Compliance and standards are met as per the company policy. SAP HANA enables the customer to implement different security policies and procedures and to meet compliance requirements of the company.
SAP HANA encourages multiple databases in a single HANA system and it is recognized as multitenant database containers. HANA system also contains more than one multitenant database containers.

Multiple container systems always have exactly one system database and any number of multitenant database containers.
SAP HANA presents all security associated characteristics such as Authentication, Authorization, Encryption, Auditing, and some add-on features, which are not approved in other multi-tenant databases.
SAP HANA security related features are given below:
- User and Role Management.
- Authentication and SSO.
- Authorization.
- Encryption of data communication in Network.
- Encryption of data in Persistence Layer.
User and Role Management:
SAP HANA User and Role management configuration depend on the architecture as below.
i. 3-Tier Architecture.
ii. 2-Tier Architecture.
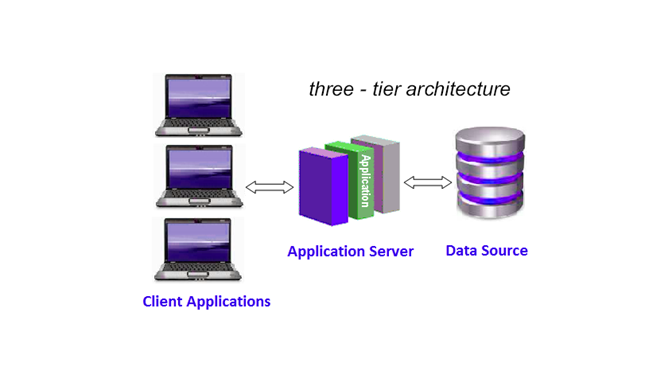
i. 3-Tier Architecture:
SAP HANA can be used as a relational database is a 3-Tier Architecture.
In this architecture, security features (authorization, authentication, encryption, and auditing) are installed on application server layers.
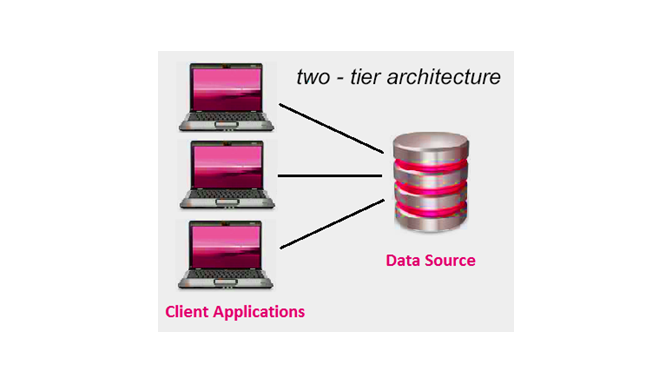
ii. 2-Tier Architecture:
SAP HANA Extended Application Services (SAP HANA XS) is based on 2 –Tier Architecture, in which Application server, Web Server and Development Environment are embedded in a single system.
Authentication and SSO:
Database user recognizes who is accessing the SAP HANA Database. It is verified through a process Named “Authentication.” SAP HANA support many authentication methods. Single Sign-on (SSO) is used to integrate several Authentication methods.
SAP HANA supports following authentication methods:
- Kerberos.
- User Name / Password.
- Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML).
- SAP Logon and Assertion Tickets.
- X.509 Clients Certificates.
Authorization:
SAP HANA Authorization is desired when a user using client interface (JDBC, ODBC, or HTTP) to access the SAP HANA database.
Depending on the authorization provided to the user, it can perform database operations on the database object. This authorization is called, “privileges.”
The Privileges can be granted to the user directly or indirectly (through roles). All Privileges assign to users are combined into a single unit.
In SAP HANA types of privileges are given below there:
- System Privileges.
- Object Privileges.
- Analytic Privileges.
- Package Privileges.
- Application Privileges.
- Privileges on User.
Encryption of data communication in the network:
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) are supported and recommended for network communication where possible.
Encryption of data persistence layer:
Data volume encryption secures that anyone can access the data volume on disk using operating system commands cannot see the actual data.
Auditing: Actions performed in the SAP HANA database can be audited.
In next, blog we have given clear structure for SAP HANA Training & Certification.

Chandanakatta
Author
Hey there! I shoot some hoops when I’m not drowned in the books, sitting by the side of brooks.