Best Guide to know more about “The Big Data”.
Introduction to Big Data
To understand Big Data, first you need to understand “What is Data“?
Data is a set of values of qualitative or quantitative variables. Pieces of data are individual pieces of information.
Now what is “Big Data”?
The term Big Data can be described as collection of data that is huge in size and yet growing exponentially with time.
In short, such a data is so large and complicated that none of the common data management tools are able to store it or process it efficiently.
Big Data can be divided into 3 categories:
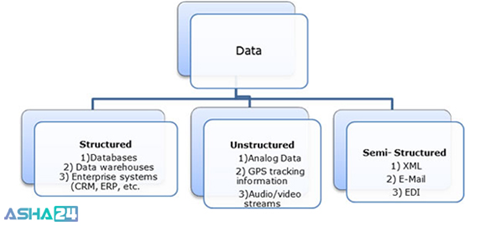
(1) Structured: Structured Data is used to refer to the data which is already collected in databases, in an ordered manner. It considers for about 20% of the total actual data, and is used the most in programming and computer-related projects.
(2) Unstructured: Structured data occupies in the regular row-column databases, while unstructured data is the opposite. They have no clear format in Data Lake. About 80% of the data created of total account for unstructured big data. We mostly encounter this data. Until recently, there was not much to do to it except storing it or explaining it manually.
(3) Semi-Structured: Semi-structured data can contain both the forms of data structured and unstructured as well. Information that is not in the traditional database format as structured data, but contains organizational properties is included in semi-structured data.
Characteristics of Big Data:
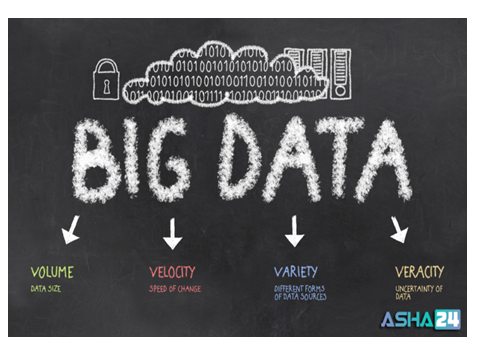
While there are plenty of descriptions for big data, most of them include the theory of what’s usually known as “four V’s” of big data:
Volume:
In today’s world there many organization that produces and processes data ranging from terabytes to petabytes. All this high volume of data needs to be captured and analyzed in order to add value to decision making process.
Few examples of organizations that deals with high data volume
Twitter – needs to analyze around 12 TB of data every day
Annual meter reading orgs needs to analyze 350 billion meter reading in order to predict the power consumption.
Velocity:
The data is growing rapidly. It is considered that the volume of data will double in every 2 years.
Variety:
The data created is completely different in the sense that it could be in multiple formats like video, text, database, numeric, and sensor data. So learning the type of Big Data is a key factor to unlocking its value.
Veracity:
The variety of sources and the complexity of the processing can lead to difficulties in judging the nature of the data (and consequently, the nature of the resulting report)
How does a Big Data Life Cycle look like?
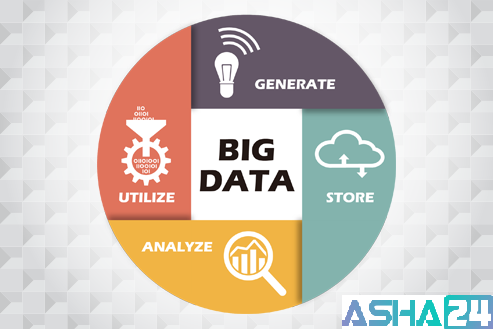
Approach to implement big data can differ; there are some common strategies and software that we can talk about generally. While the steps shown below might not be true in all cases, they are widely used.
(1) Data Acquisition – Big data solutions intelligently processes the raw input data to generate accurate metadata that describes what data is captured and measured.
(2) Data Analytics – Normally the data that is captured is not ready for analysis. A process is required that extracts only the required information from the underlying sources and expresses it in a format that is suitable for analysis.
(3) Data Awareness – With wide variety of data, it is not enough to just store data in repository. Data needs to be integrated in such a manner so that it provides considerable amount of information that could be used further down for relevant data analysis.
Benefits of Big Data:
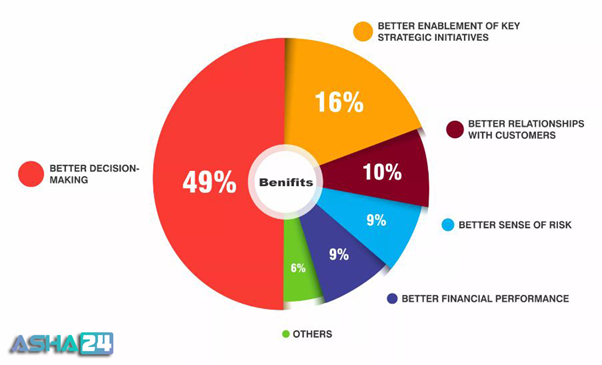
Understanding process of ‘Big Data’ brings in multiple benefits, such as-
(1) Businesses can employ outside intelligence while taking judgments
Introduction to social data from search engines and sites like Facebook, twitter are allowing businesses to fine tune their business plans.
(2) Improved customer service
Regular customer feedback methods are getting replaced by new systems created with ‘Big Data’ technologies. Big Data and simple language processing technologies are being used to read and decide consumer responses.
(3) Quick identification of risk to the product/services, if any
(4) Better operational performance
Big data systems are uniquely suited for surfacing difficult-to-detect models and presenting insight into actions. Organizations can gain incredible value from data that is already available by accurately implement systems which deal with big data.
If you like this article, and wish to know more on Big Data, click here and read up.

Mahesh J
Author
Hello all! I’m a nature’s child, who loves the wild, bringing technical knowledge to you restyled.